| extras | ||
| pics | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| beidou.txt | ||
| galileo.txt | ||
| glo-ops.txt | ||
| gnss.txt | ||
| gps-ops.txt | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
| requirements.txt | ||
| tle2ssc | ||
Spacecruft Celestia GNSS
Celestia is a "real-time space simulation that lets you experience our universe in three dimensions".
The present repo contains the tle2ssc Python script which converts
NORAD Two-Line Element sets (TLE) from CelesTrak into into
Solar System Catalog (SSC) files that can be read by Celestia.
The tle2ssc script is set by default to retrieve the latest orbits
for various GNSS ("GPS") satellite systems.
It could be easily updated for any other source of TLEs.
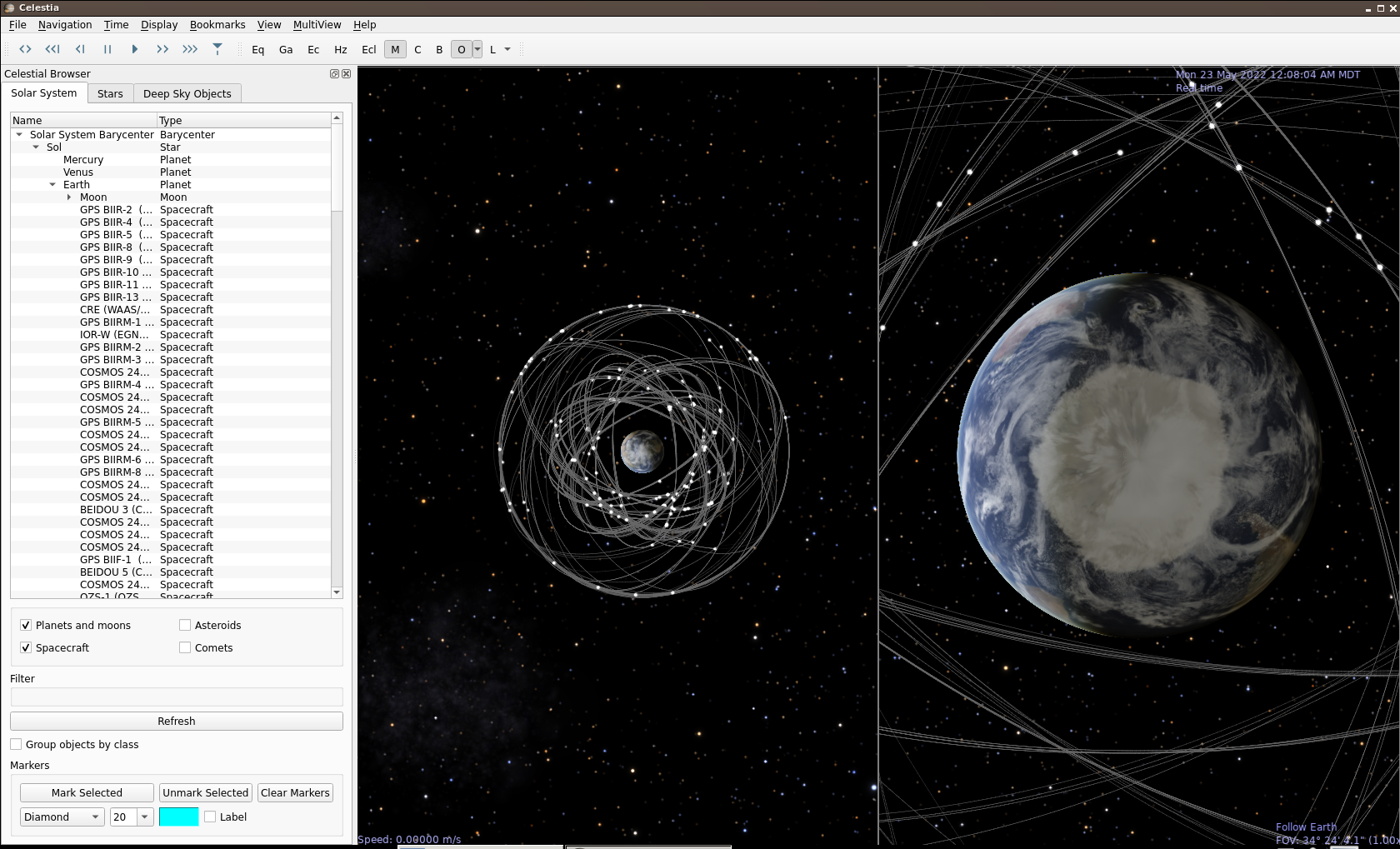
Celestia Animated Time Lapse GNSS Orbits
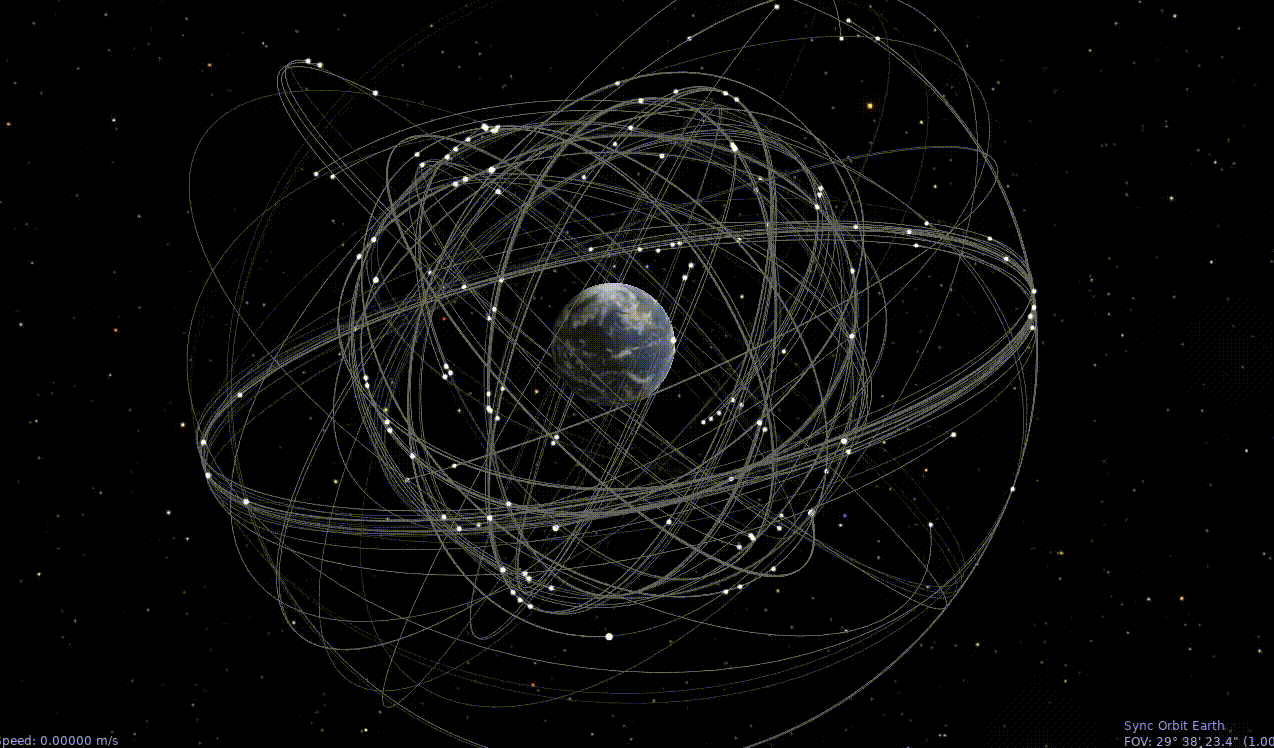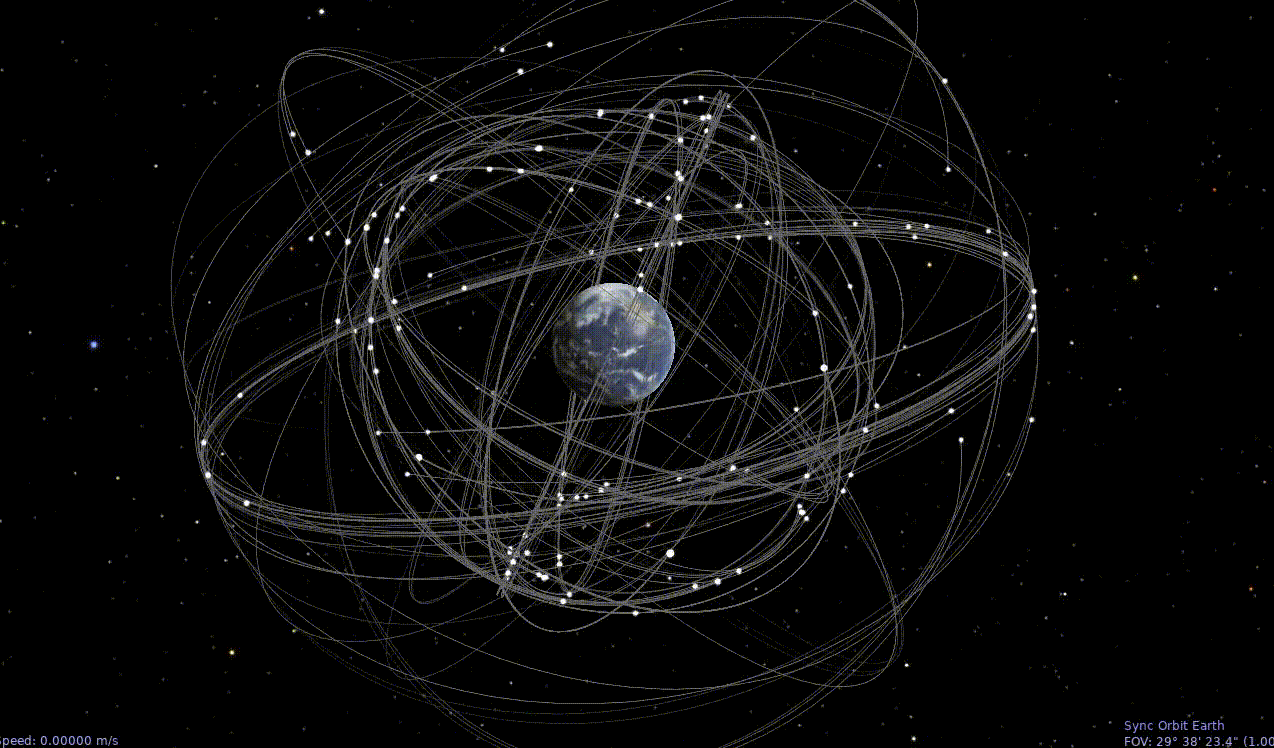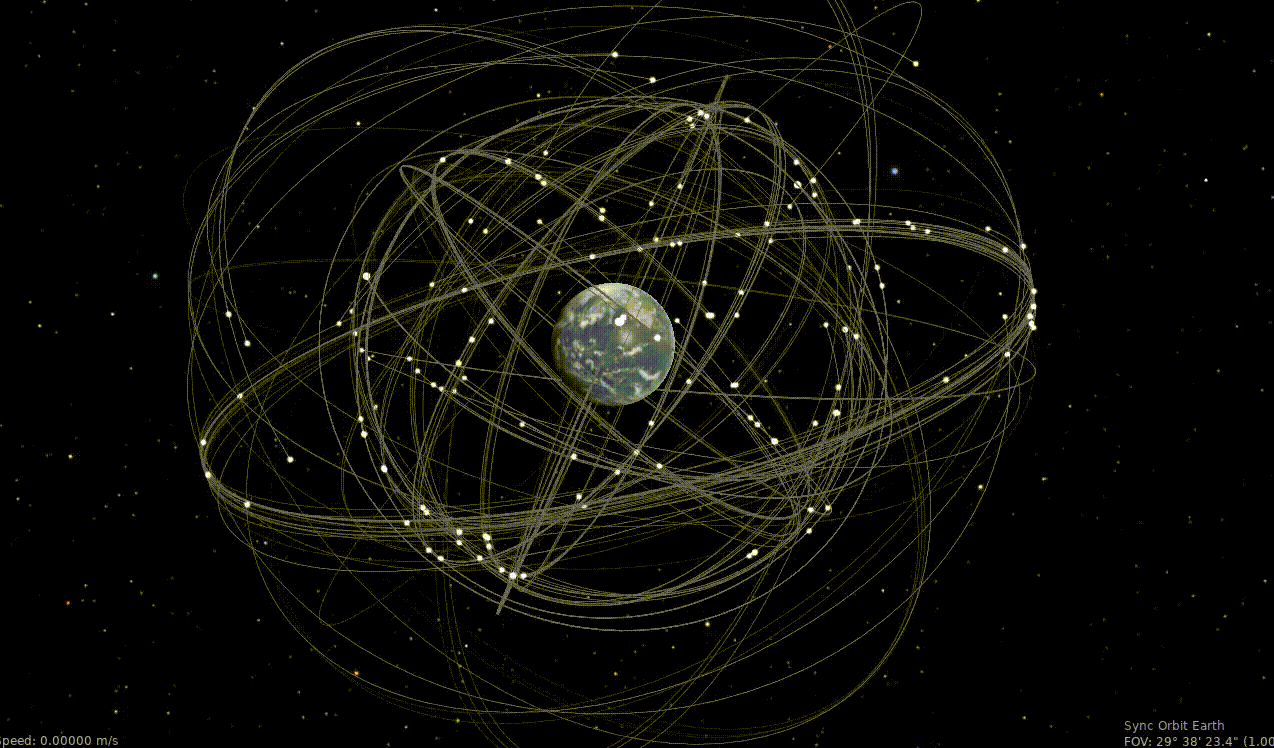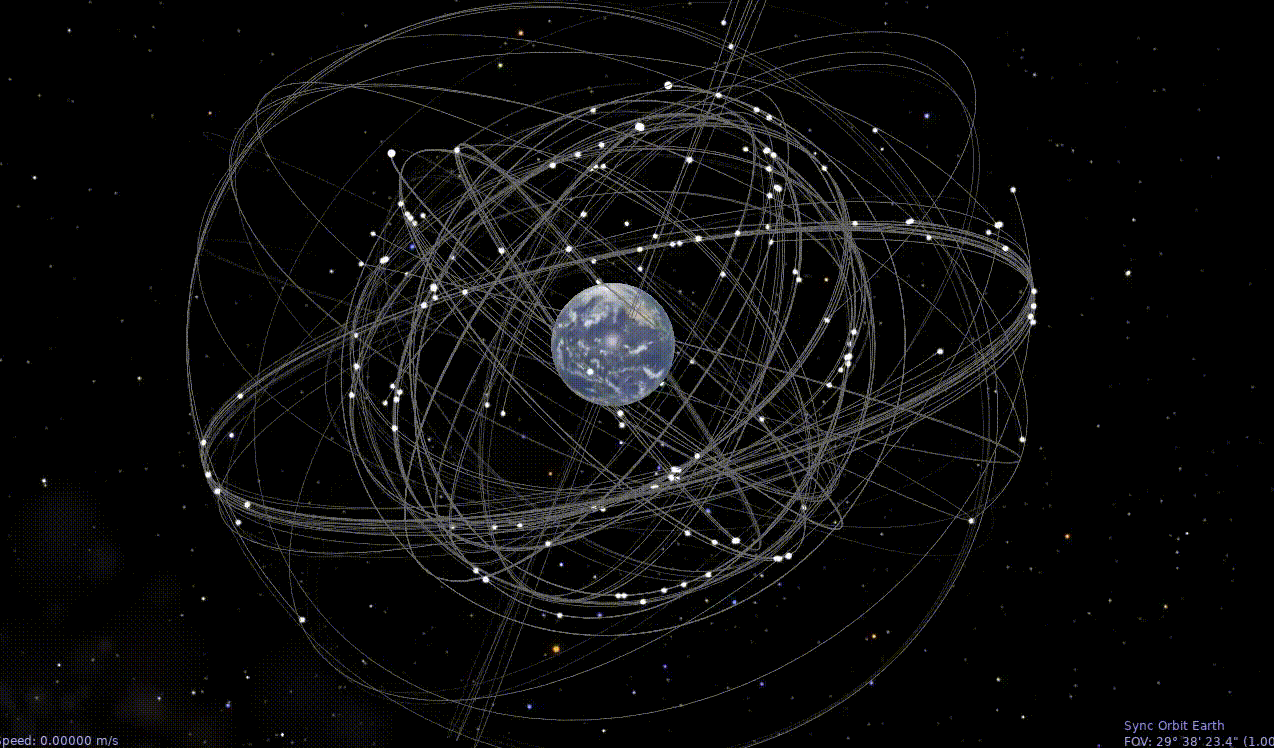
Quick & Dirty Install
If you just want to import the pre-generated file into Celestia for
a look, just copy these files into your extras folder or similar.
# crufty below, private dir better
sudo mkdir -p /usr/share/celestia/extras-standard/gnss/models/
# Whatever user...
sudo chown -R debian:debian /usr/share/celestia/extras-standard/gnss
# Get SSC file
wget -O /usr/share/celestia/extras-standard/gnss/gnss.ssc \
https://spacecruft.org/spacecruft/celestia-gnss/raw/branch/main/extras/gnss/gnss.ssc
# Get 3D model
wget -O /usr/share/celestia/extras-standard/gnss/models/galileo-gnss.cmod \
https://spacecruft.org/spacecruft/celestia-gnss/raw/branch/main/extras/gnss/models/galileo-gnss.cmod
# Then (re)start Celestia.
Install celestia-gnss
Install thusly to generate your own .ssc files.
git clone https://spacecruft.org/spacecruft/celestia-gnss
cd celestia-gnss
sudo apt update
sudo apt install python3-pip python3-virtualenv
# Many ways to do python setup, here is one:
virtualenv -p python3 env
source env/bin/activate
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -r requirements.txt
Run celestia-gnss
Example (crufty example, if you have perms):
./tle2ssc > /usr/share/celestia/extras-standard/gnss/gnss.ssc
Use in Celestia
Use thusly, hooman.
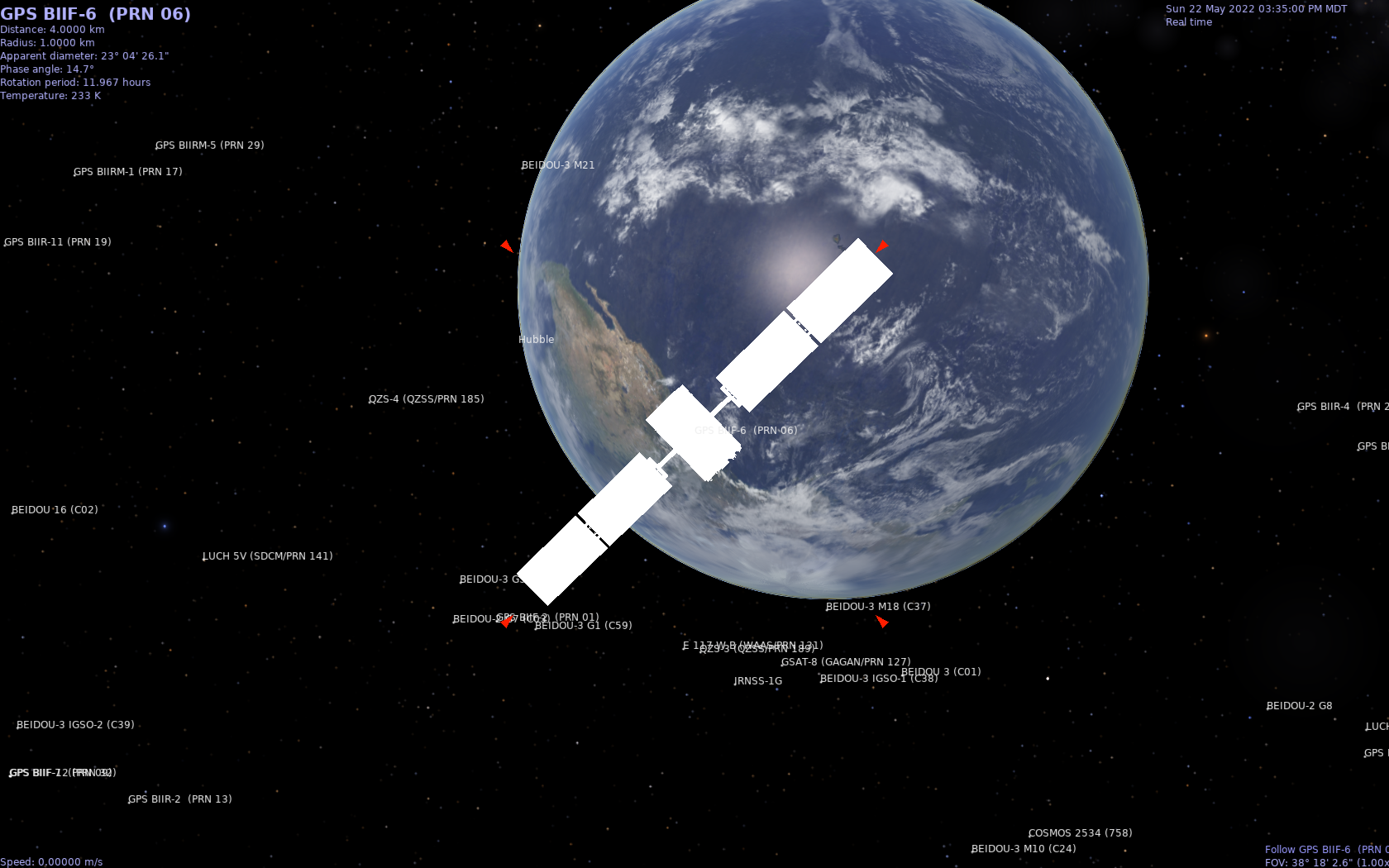
Celestia Showing GNSS Satellites with Labels
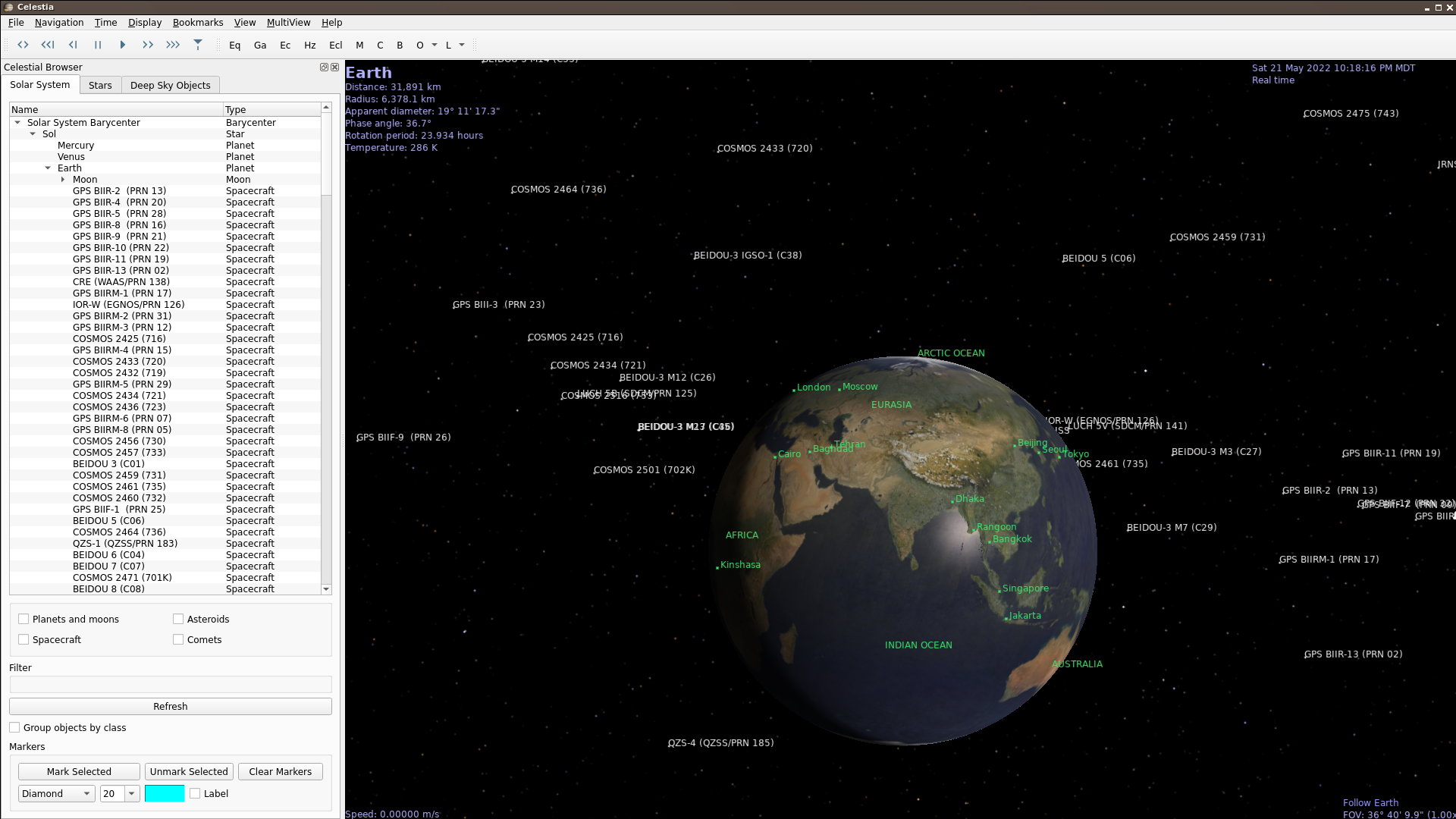
Then copy the satellites you want into your Celestia extras dir. Crufty bad way to do it, example:
sudo cp -a extras/gnss/gnss.ssc /usr/share/celestia/extras-standard/
Each system, GPS, Galileo, Glonass, Beidou, can be used, or the GNSS files which include all four, plus more regional systems.
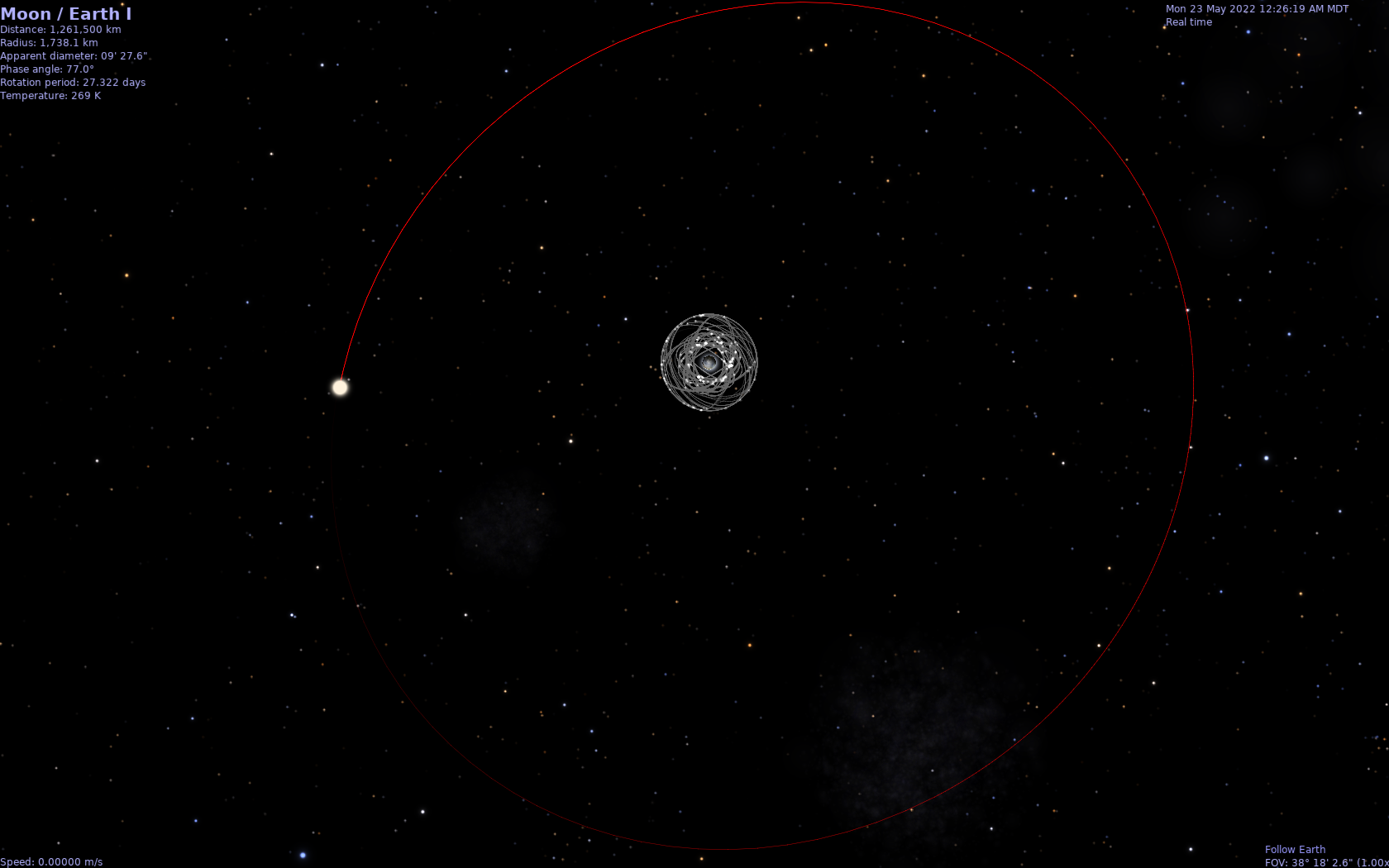
Screenshots
Screenshots of running Celestia with GNSS satellites.
GNSS Satellites Orbiting Earth
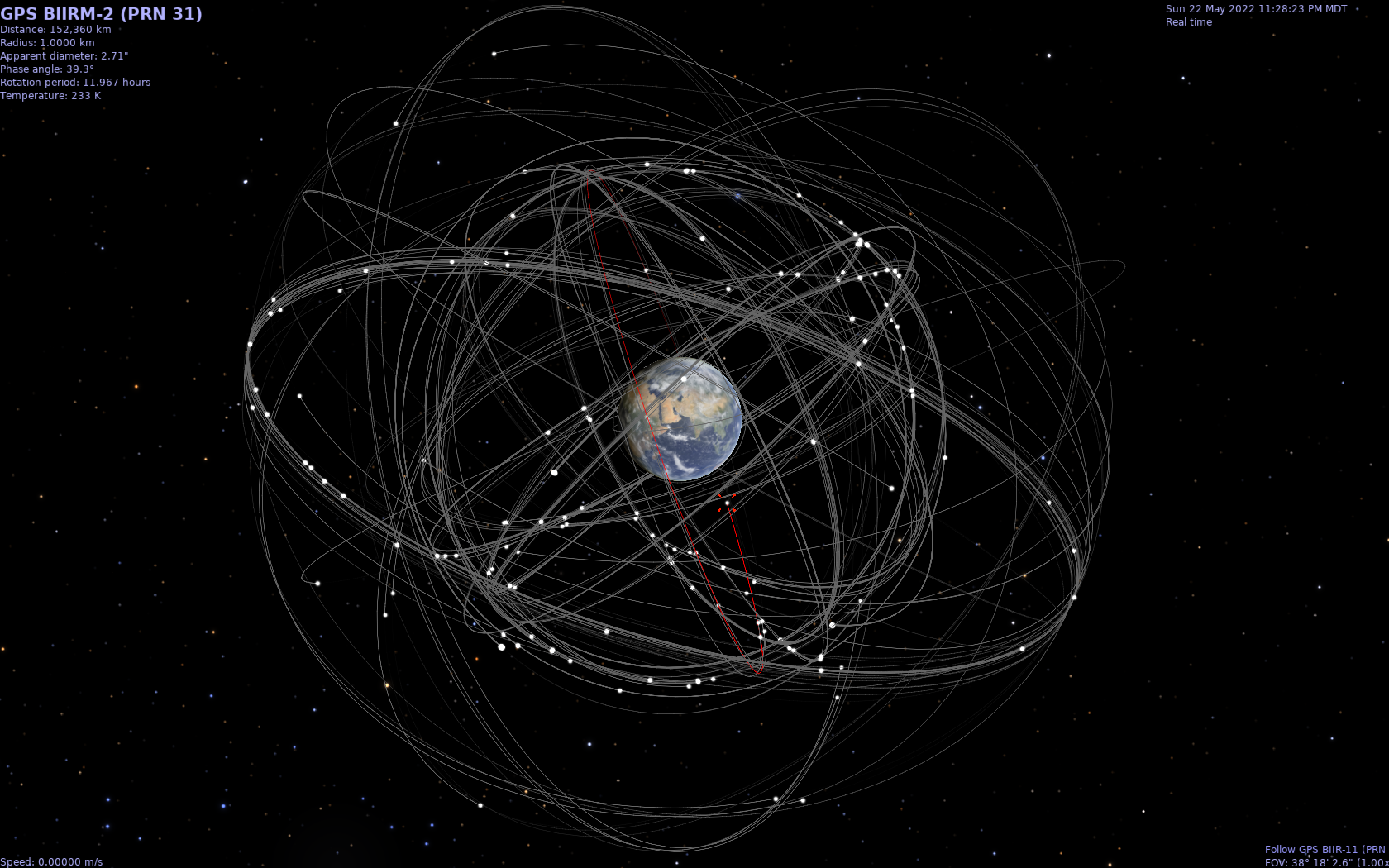
Celestia with Moon orbit, Earth, and GNSS satellites.
See Also
Spacecruft
Spacecruft:
Celestia
Upstream Celestia:
Celestia forum thread about celestia-gnss:
TLE Conversion
TLE Conversion Spreadsheet by Grant Hutchison from July 2003,
the basis for the formulas in the tle2ssc script.
-
https://www.classe.cornell.edu/~seb/celestia/hutchison/spreadsheets.html
-
https://www.classe.cornell.edu/~seb/celestia/hutchison/tle-xls.zip
Useful formula from here too:
I had this exact printout on my desk (trimmed to size!) when I came across this gem from @fisadev via Poliastro docs:
How are satellite orbits disseminated?
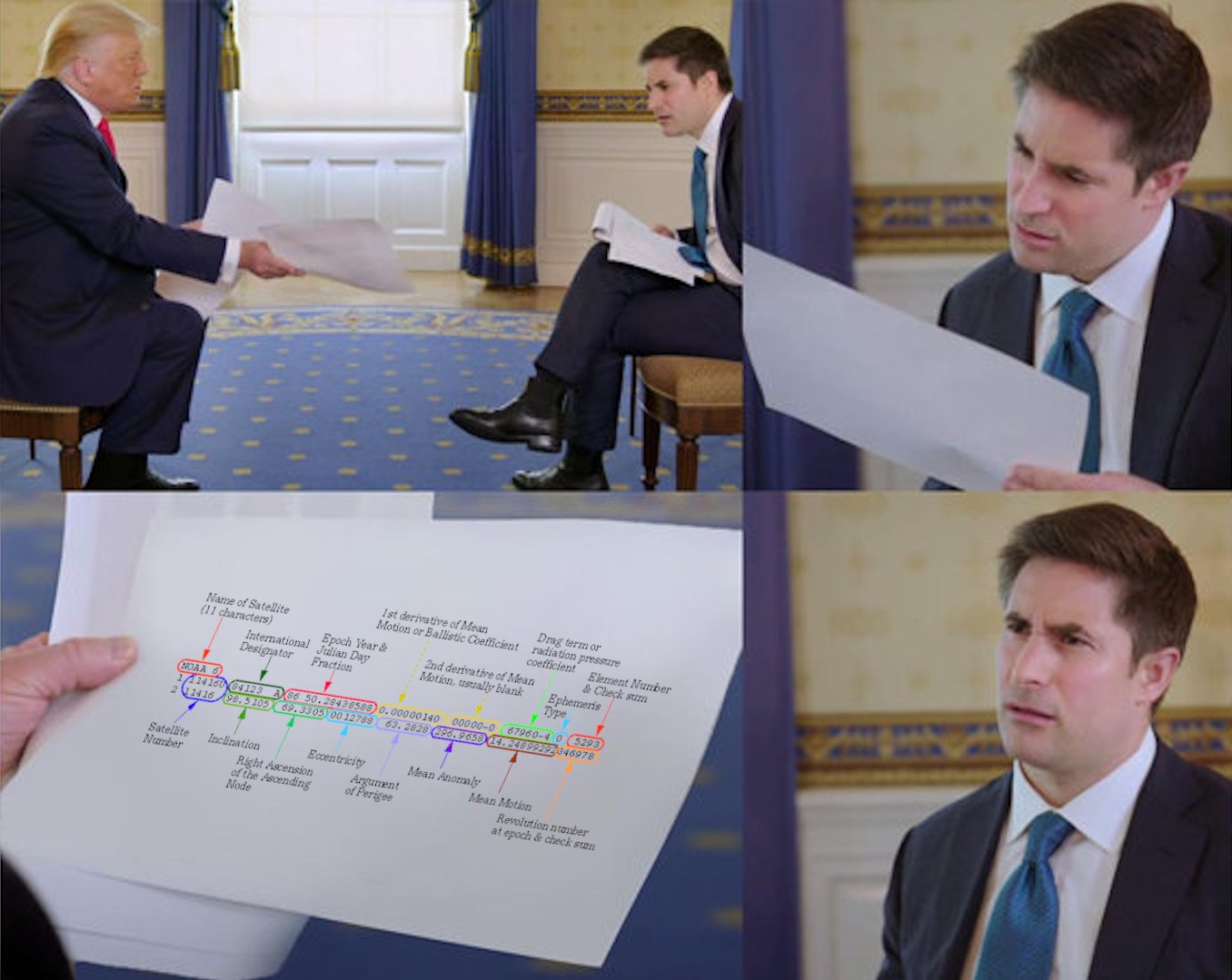
Perhaps from page 7 of the PDF, Strategic Center for Networking, Integration, and Communications Orbit Propagation Front-End Software Development.
Not used, but perhaps could be useful from Libre Space Foundation:
Solar System Catalog
"Solar System Catalog" files are primarily used to define the objects which can be found in a stellar system, such as planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and spacecraft. They also have four other uses: they can define alternative surface textures, locations on or near an object, and orbital reference points. An SSC file can also edit objects which have been defined in other SSC catalog files.
Info on .ssc files:
In Celestia the name "Galileo" is used for the other spacecraft, not
for the EU GNSS. So the name used in here adds -gnss,
ala, galileo-gnss.ssc, whereas the other GNSS don't have it appended.
Example .ssc file contents:
"GSAT0101 (PRN E11)" "Sol/Earth" {
Class "spacecraft"
Mesh "galileo-gnss.cmod"
Radius 0.005
EllipticalOrbit {
Epoch 2459722.35154914
Period 0.58659637
SemiMajorAxis 29600.176
Eccentricity 0.00041090
Inclination 56.9865
AscendingNode 22.0582
ArgOfPericenter 29.0248
MeanAnomaly 331.0391
}
Obliquity 56.9865
EquatorAscendingNode 22.0582
RotationOffset 296.9294
# Orientation [ ]
}
TLE Sources
GNSS (All)
Beidou (China)
Galileo (Europe)
Glonass (Russia)
GPS (USA)
Spice
Spice TLE: "Evaluate NORAD two-line element data for earth orbiting spacecraft."
SGP4
SPG4
Skyfield
Skyfield
3D Models
Celestia uses an old 3D proprietary format from an old 3D application in
.3ds format. It also has it's own format .cmod.
Galileo
Galileo 3D models are from the ESA:
3D Model Conversion
The galileo.obj file from the ESA can be read by cmodview in
the celestia-tools package. The file can be saved in cmodview
as galileo-gnss.cmod and then read by Celestia.
The ESA supplies textures, but the aren't applied in the Celestia model (yet).
Blender
blender-2.79b didn't work to convert a .obj file to .3ds
that rendered in Celestia.
TODO
Do.
-
All GNSS satellites are using the Galileo 3D model.
-
Textures need to be added to 3D models.
-
Orientation of satellite 3D models is incorrect.
-
Confirm orbits are reasonably correct.
Status
Alpha, under development.
Output works in Celestia. Orbits are not confirmed correct.
License / Copyright
Upstream sources under their respective copyrights.
Copyright (C) 2022, 2023 Jeff Moe.
License: GPLv2 or any later version.