| examples | ||
| img | ||
| notebooks | ||
| template | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
| requirements-dev.txt | ||
| requirements.txt | ||
| witzit-load | ||
| witzit-plot | ||
| witzit-plot2png | ||
witzit - What In The Zap Is That?
witzit --- What In The Zap Is That?
AI categorization of spectra from LIBS/XRF analyzers.
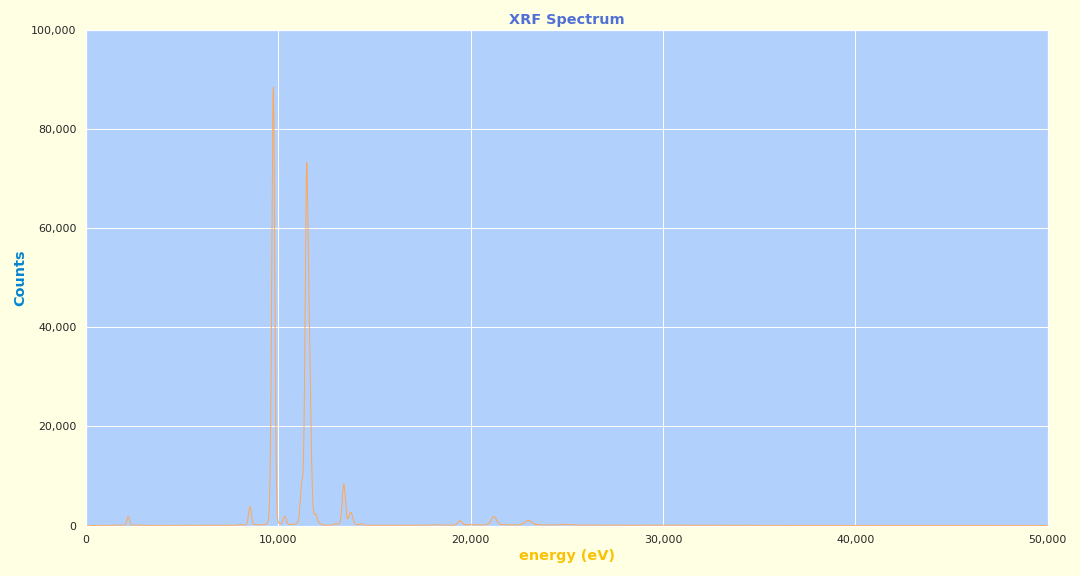
Example Jupyter plot from SciAps X-555 XRF:
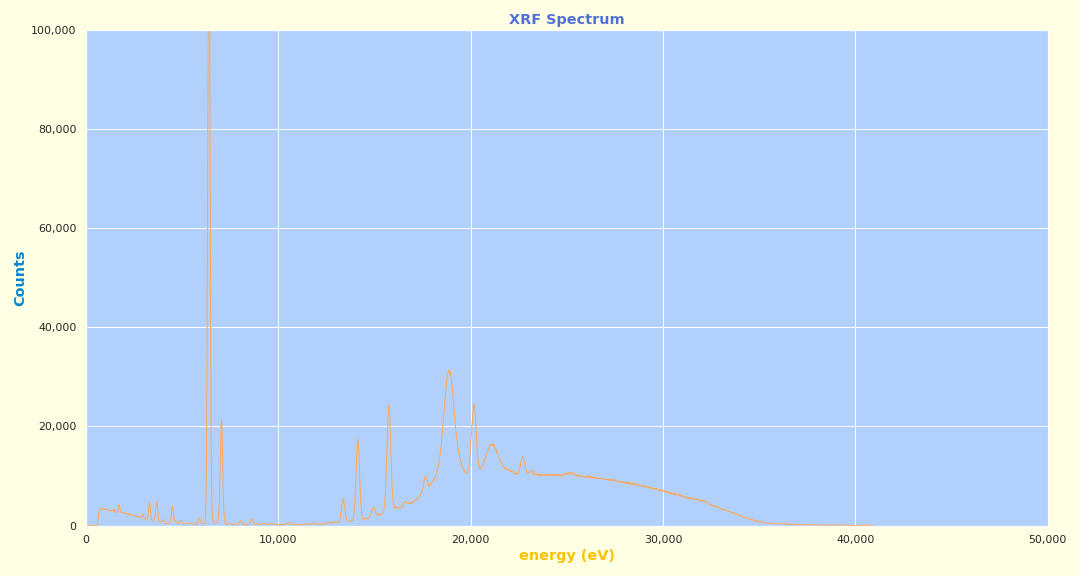
Example plot from Olympus Vanta XRF:
Install
Install Dependencies
Get system dependency and upgrade Python pip. Perhaps do something like this, or set up a Python virtual environment.
sudo apt update
sudo apt install git python3-pip python3-virtualenv
pysalx
The pysalx repo contains scripts for interacting with the device.
Install that too.
git clone https://spacecruft.org/spacecruft/pysalx.git
cd pysalx/
# Set the date
./scripts/pysalx-date-set
# whatever else...
..
Clone Git Repo
Get source code with git.
The default requirements.txt installs a Tensorflow without
GPU support. You can edit the requirements.txt file to change
which is supported. The "generic" version supports both.
XXX tensorflow not available in pip 2023-01.
Setup
Thusly.
git clone https://spacecruft.org/spacecruft/witzit
cd witzit/
virtualenv -p python3 env
source env/bin/activate
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -r requirements.txt
deactivate
witzit scripts
witzit-load--- Load and text display data from SciAps or Olympus XRF.witzit-plot--- Plot a sample from a SciAps X-555 or Olympus Vanta-M.witzit-plot2png--- Plot a sample from a SciAps X-555 or Olympus Vanta-M and save to PNG.
Development is most easily done under Jupyter with Tensorboard
for training models. These files are in the notebooks/ directory.
witzit-plot.ipynb--- witzit Jupyter notebook, plotting application for SciAps X-555 or Olympus Vanta-M.witzit-predict.ipynb--- witzit Jupyter notebook, prediction application.witzit-train.ipynb--- witzit Jupyter notebook, training application.
Data
Note: Files in the data/ directory may be deleted and/or manipulated
by scripts in this application.
Note well, the data/ directory is ignored by git, and is a temporary
directory where data to be processed is stored. For example, if you have
a main original archive of 10,000 samples and you want to process just 1,000
of them, they would be copied to the data/ directory.
Data is also stored here, which can also be deleted/moved by scripts:
/srv/witzit/
Each element sample will be stored under here:
/srv/witzit/data/element/
Each element model will be stored under here:
/srv/witzit/data/models/
Temporary logs during training may be written to the gitignored
logs/ directory.
Usage
HOWTO USE. Getting closer...
# Example:
debian@workstation:~/spacecruft/witzit$ ./witzit-load-x555
energy (eV) 2048
0 20.590676 0
1 45.021816 0
2 69.452957 0
3 93.884097 0
...
1023 25013.647367 175
1024 25038.078508 173
1025 25062.509648 155
1026 25086.940789 193
...
2047 50031.135199 1
Jupyter Notebooks
Run jupyter thusly:
cd witzit/notebooks
jupyter-lab
Hardware
-
SciAps LIBS Analyzer
-
SciAps XRF Analyzer
-
Olympus XRF Analyzer
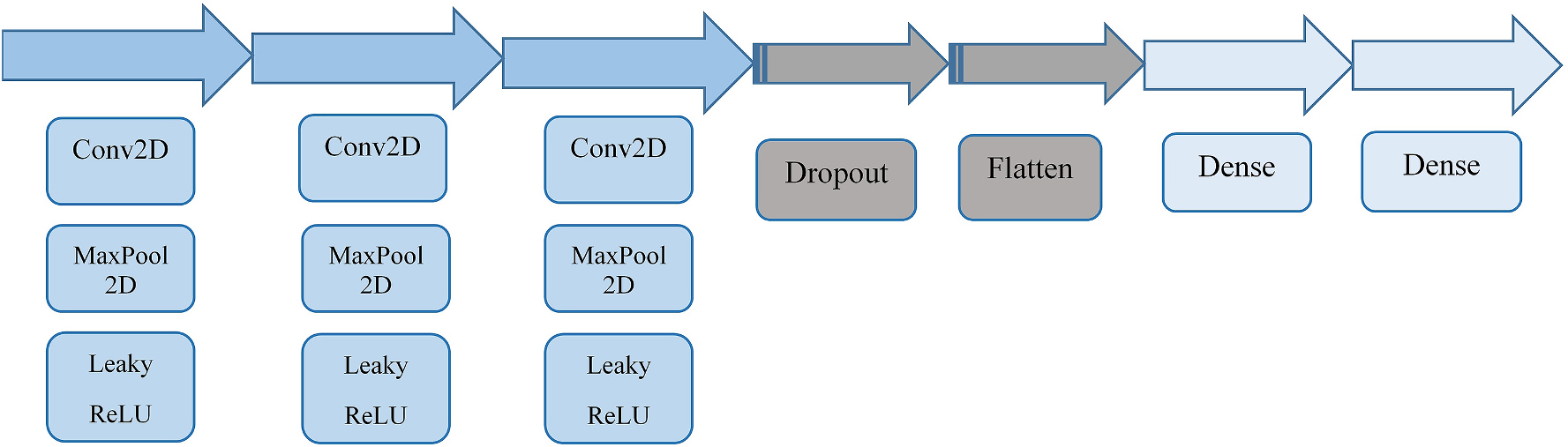
Deep Learning Algorithm
Can use lots from wut.
def uncompiled_model():
model = Sequential([
Conv2D(16, 3, padding='same', activation='relu', input_shape=(IMG_HEIGHT, IMG_WIDTH ,3)),
MaxPooling2D(),
Conv2D(32, 3, padding='same', activation='relu'),
MaxPooling2D(),
Conv2D(64, 3, padding='same', activation='relu'),
MaxPooling2D(),
Flatten(),
Dense(512, activation='relu'),
Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')
])
return model
Amazingly (to me), the paper
Classification of radioxenon spectra with deep learning algorithm
(2021) by Azimi, et al. uses nearly the identical CNN Sequence() as
wut uses, indicating it may be a very good base to start from.
Paper is non-gratis science:
The Sequence() diagram is pulled from the Azimi paper, but is the
same as in wut, so makes a good reference.
Articles:
-
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0265931X21001909 Classification of radioxenon spectra with deep learning algorithm
-
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0030401822000402 Deep convolutional neural networks as a unified solution for Raman spectroscopy-based classification in biomedical applications
-
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S058485472030313X Automatic preprocessing of laser-induced breakdown spectra using partial least squares regression and feed-forward artificial neural network: Applications to Earth and Mars data
-
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0584854719306068 Determination of minor metal elements in steel using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy combined with machine learning algorithms
-
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1386142521009380 Feature selection of infrared spectra analysis with convolutional neural network
Development
Setup like above, and also:
cd witzit/
source env/bin/activate
pip install -r requirements-dev.txt
Then before committing new code, make sure it is enprettified:
black foo.py
See Also
pysalx--- Unofficial scripts for interacting with the SciAps LIBS and XRF analyzers.
https://spacecruft.org/spacecruft/pysalx/
wut?--- What U Think? SatNOGS Observation AI.
https://spacecruft.org/spacecruft/satnogs-wut/
Status
Alpha software under development. Need to check:
- API: 501 Not Implemented spacecruft/pysalx#2
Unofficial
Unofficial, unaffiliated with SciAps or Olympus.
License
License: GPLv3 or any later version.
Copyright © 2019-2023, Jeff Moe.